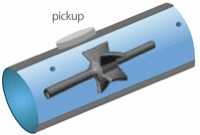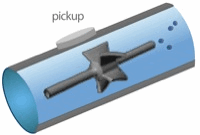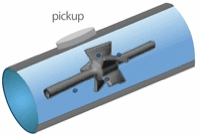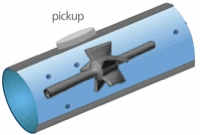
From the foregoing historical review, many flowmeter technologies and designs have evolved in order to cover the vast number of applications. These range from flow of blood in small arteries to the flow in rivers and canals, from cryogenic liquids up to high temperature gases, and from below atmospheric pressure to conditions inside high-pressure industrial reactors lace wigs uk. The operating conditions and applications often dictate the choice of technology. The table below summarizes the enormous range of operating parameters. These have been conveniently split into closed pipe and open channel applications.
“operating conditions” for flowmeters
| In closed pipe lines | |
| Flow rates | 0.1 g/h to 5000 t/s (0.0002 lb/h to 5500 t/s) |
| Nominal diameters (pipe diameters) | 0.1 mm to 15 m (0.004 in to 50 ft) |
| Pressures | vaccum to 3000 bar (43500 psi) |
| Temperatures | -250 to +800 ?C (-418 to 1470 ?F) |
| Fluids (medium) | liquids, gases, steam, fluid mixtures |
| In Open channels (channels, rivers, etc.) | |
| Line sizes | 50 mm (2 inch) to “river size”, ocean current and point measurements |
| Temperatures | normal ambient temperature |
The two following illustrations give some indications of the flowmeters and metering methods in common use today. As indicated, most meters measure the volume of flow of the fluid velocity. Flowmeters in closed pipes – as opposed to open channels – constitute the majority of applications.
Flow measurement (in closed pipes) 70%
Fluids 65%, Gases/ mixtures 35%
| Volume Flow Measurements | |
| Direct method | Positive Displacement |
| Indirect method | Differential Pressure, Variable area, Turbine, Vortex, Electromagnetic, Ultrasonic, Pitot tube, others |
| Mass Flow Measurements | |
| Direct method | Coriolis principle, Thermal principal, Weighing systems, Solid type meters |
| Indirect method | Multivariable type |
| Flow measurement (in open lines) 30% | |
| Fluids 95%, Solids/slurries 5% | |
| Flumes | Parshall, Palmer-Bowlus, Khafagi, rectangular/ Trapezoidal ( with/without restrictions), Special flumes |
| Weirs | Triangular (V shaped), rectangular/ Trapezoidal ( with/without restrictions) |
Other methods Velocity- area method (current meter, ultrasonic), Level Measurement (Ultrasonic, DP, Float, etc..), Solid type meters.